Navigating Human Resource Challenges and Key Success Factors in the Transition to Integrated Logistics Systems: A Change Management Perspective
Downloads
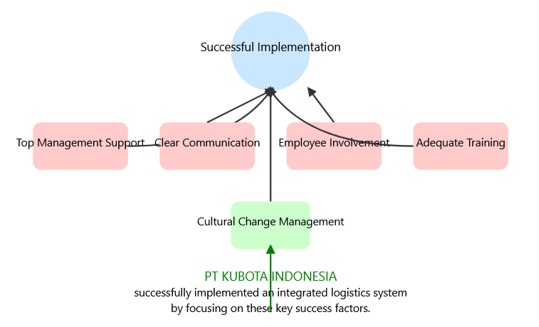
This study examines the process of change management, identifies human resource obstacles, and explores critical success factors in deploying an integrated logistics system at PT Kubota Indonesia. Employing a qualitative approach and case study methodology, data were gathered via semi-structured interviews, observations, and document analysis. Findings reveal that PT Kubota Indonesia employs a systematic change management strategy that considers human and cultural dimensions. Despite encountering challenges like deficiencies in technical expertise and resistance to change, the company effectively addressed these issues through proactive communication, staff engagement, training initiatives, and strong management backing. Key drivers of success identified encompass executive support, transparent communication, employee involvement, comprehensive training, and adept cultural change management. This study contributes insights into a comprehensive approach to change management, emphasizing the synchronization of technical aspects with human and cultural factors to ensure the triumphant integration of an advanced logistics system.
Downloads
[1] S. Bag, S. Gupta, and L. Wood, "Big data analytics in sustainable humanitarian supply chain: Barriers and their interactions," Annals of Operations Research, vol. 319, no. 1, pp. 721-760, 2022.
[2] K. Govindan, S. G. Azevedo, H. Carvalho, and V. Cruz-Machado, "Impact of supply chain management practices on sustainability," Journal of Cleaner production, vol. 85, pp. 212-225, 2014.
[3] D. Chrusciel and D. W. Field, "Success factors in dealing with significant change in an organization," Business Process Management Journal, vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 503-516, 2006.
[4] M. T. Siregar and T. Mutiara, "Perbaikan Proses di Dalam Gudang Mengunakan Metode DMAIC Pada PT. Dakota Logistik Indonesia," Praxis: Jurnal Sains, Teknologi, Masyarakat dan Jejaring, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 139-150 %@ 2622-9137, 2019.
[5] E. Hofmann, H. Sternberg, H. Chen, A. Pflaum, and G. Prockl, "Supply chain management and Industry 4.0: conducting research in the digital age," International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, vol. 49, no. 10, pp. 945-955, 2019.
[6] D. Hwang, M. G. M. Yang, and P. Hong, "Mediating effect of IT-enabled capabilities on competitive performance outcomes: An empirical investigation of ERP implementation," Journal of Engineering and Technology Management, vol. 36, pp. 1-23, 2015.
[7] S. Sabil, A. Djakasaputra, B. A. Bangkara, S. O. Manullang, and P. Hendriarto, "Understanding Business Management Strategies in Enhancing Profitable and Sustainable SMEs," Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 112-131 %@ 2598-5795, 2022.
[8] P. Ruivo, T. Oliveira, and M. Neto, "Examine ERP post-implementation stages of use and value: Empirical evidence from Portuguese SMEs," International journal of accounting information systems, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 166-184, 2014.
[9] J. Stoffers, P. Neessen, and P. van Dorp, "Organizational culture and innovative work behavior: A case study of a manufacturer of packaging machines," American Journal of Industrial and Business Management, vol. 5, no. 04, p. 198, 2015.
[10] I. Zai, Y. Yulianti, S. Feblicia, A. L. Z. Aqmi, and A. F. Rahmah, "Analisis Pengaruh Peningkatan Kinerja, Incoterms, Transportasi, Distribusi, Keterlibatan TPL dan Manajemen Risiko Terhadap Aktivitas Logistik," Jurnal Sosial Teknologi, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 225-238, 2022.
[11] R. Hasanaj and A. M. Manxhari, "Importance of communication during change: A case of the municipality of Vlora," European Journal of Multidisciplinary Studies, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 15-19, 2017.
[12] M. Ali, L. Zhou, L. Miller, and P. Ieromonachou, "User resistance in IT: A literature review," International Journal of Information Management, vol. 36, no. 1, pp. 35-43, 2016.
[13] T. Hackman, "Leading change in action: Reorganizing an academic library department using Kotter’s eight stage change model," Library Leadership & Management, vol. 31, no. 2, 2017.
[14] H. Kotzab, C. Teller, M. Bourlakis, and S. Wünsche, "Key competences of logistics and SCM professionals–the lifelong learning perspective," Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 50-64, 2018.
[15] M. Nasiri, J. Ukko, M. Saunila, and T. Rantala, "Managing the digital supply chain: The role of smart technologies," Technovation, vol. 96, p. 102121, 2020.
[16] V. Amarantou, S. Kazakopoulou, D. Chatzoudes, and P. Chatzoglou, "Resistance to change: an empirical investigation of its antecedents," Journal of Organizational Change Management, vol. 31, no. 2, pp. 426-450, 2018.
[17] S. F. Wamba, M. M. Queiroz, and L. Trinchera, "Dynamics between blockchain adoption determinants and supply chain performance: An empirical investigation," International Journal of Production Economics, vol. 229, p. 107791, 2020.
[18] M. M. Queiroz, S. C. F. Pereira, R. Telles, and M. C. Machado, "Industry 4.0 and digital supply chain capabilities: A framework for understanding digitalisation challenges and opportunities," Benchmarking: an international journal, vol. 28, no. 5, pp. 1761-1782, 2021.
[19] R. K. Yin, Case study research and applications. SAGE Publications US., 2017.
[20] C. A. Beatty, "Communicating during an organizational change," Organization Studies, vol. 15, no. 3, pp. 337-352, 2015.
[21] J. W. Creswell and C. N. Poth, Qualitative inquiry and research design: Choosing among five approaches. Sage publications, 2016.
[22] G. Li, Y. Hou, and A. Wu, "Fourth Industrial Revolution: technological drivers, impacts and coping methods," Chinese Geographical Science, vol. 27, pp. 626-637, 2017.
Copyright (c) 2024 dyah palupiningtyas, Krisnawati Setyaningrum Nugraheni, Ray Octafian

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik (Journal of Industrial and Logistics Management) is an Open Access Journal. The authors who publish the manuscript in JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik agree to the following terms:

JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. This permits anyone to copy, redistribute, remix, transmit and adapt the work provided the original work and source is appropriately cited.
This means:
(1) Under the CC-BY license, authors retain ownership of the copyright for their article, but authors grant others permission to use the content of publications in JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik in whole or in part provided that the original work is properly cited. Users (redistributors) of JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik are required to cite the original source, including the author's names, JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik as the initial source of publication, year of publication, volume number, issue, and Digital Object Identifier (DOI); (2) Authors grant JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik the right of first publication. Although authors remain the copyright owner.