KAJIAN INDUSTRI 4.0 UNTUK PENERAPANNYA DI INDONESIA
Downloads
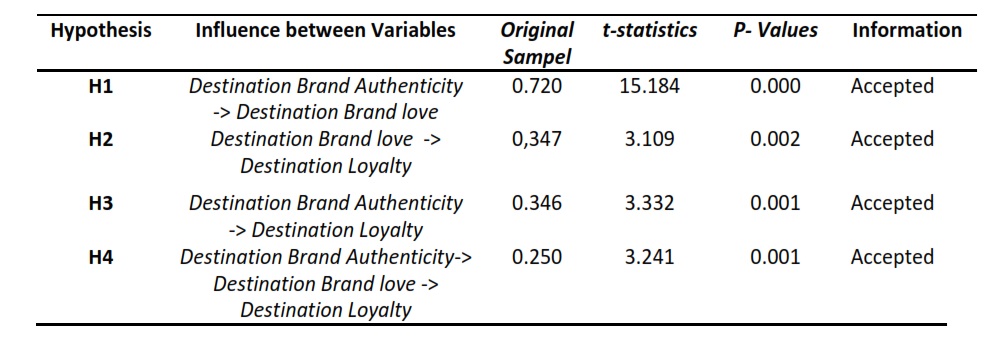
Abstract : The implementation of concept Industry 4.0 in Indonesia has been studied in this paper. The study was motivated after the launcing of Making Indonesia 4.0 by the President of the Republic of Indonesia in April 2018. The study aims to study the concept of IR 4.0 for its implementation in Indonesia. Methods include collecting various references with industry 4.0 keywords, applying information technology, pharmaceutical industry and manufacturing industries. The results of the study concluded that industry 4.0 was an era that empowered the role of manufacturing digitalization and supply networks that involved the integration of digital information from various sources and locations to drive manufacturing and distribution physically. It is found that, There are five main technologies for IR 4.0, namely Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), Wearable Technology (WT), Advanced Robotic (AR) and 3D Printing (3DP). Each component of technology can be used in various industries and manufacturing. The implementation of IR 4.0 would likely provide more benefits and advantages such as increase effieciency and effectivty in manufacturing industries.
Keywords: Concept of IR 4.0, application of information technology, manufacturing industry.
Abstrak : Telah dilakukan kajian yang mempelajari konsep Industri 4.0 (IR.4.0)untuk penerapannya di Indonesia. Kajian dilatar belakangi oleh dicanangkannya making Industri 4.0 oleh Presiden RI pada bulan April 2018. Kajian bertujuan mempelajari konsep IR 4.0 untuk implementasinya di Indonesia. Metode meliputi pengumpulan berbagai referensi dengan kata kunci industry 4.0, penerapan teknologi informasi, industru farmasi dan industry manufaktur. Selanjutnya referensi tersebut dianalisis dan diskripsi sehingga menghasilkan suatu ringkasan. Hasil kajian menyimpulkan bahwa industry 4.0 merupakan era yang memberdayakan peran digitalisasi manufaktur dan jaringan suplai yang melibatkan integrasi informasi digital dari berbagai sumber dan lokasi untuk menggerakkan manufaktur dan distribusi secara fisik. Terdapat lima teknologi utama IR 4.0, yaitu artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), Wearable Technology (WT), Advanced Robotic (AR) dan 3D Printing (3DP). Masing-masing komponen teknologi dapat dimanfaatkan pada berbagai industry dan manufaktur. Pemanfaatan IR 4.0 diyakini akan memberikan manfaat dan keuntunganyang lebih banyak (misalnya kinerja menjadi lebih efektif dan lebih efisien).
Kata kunci : Konsep IR 4.0, penerapan teknologi informasi, industry manufaktur.
Downloads
K. Bock, W. F. A. K. J.-P. Nickel, and H. Meincke. (2017, 19 Agustus 2018). Chemistry 4.0 : Growth through innovation in a transforming world. Available: https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/global/Documents/consumer-industrial-products/gx-chemistry%204.0-full-report.pdf
"Readiness for the Future of Production Report " in World Economic Forum, Switzerland, 2018.
A. Andreoni, "Industrial ecosystems and policy for innovative industrial renewal: A new framework and emerging trends in Europe," Sitra working paper2017.
A. Kearney, "Roadmap Implementasi Industry 4.0 di Indonesia," ed. Jakarta: Kementerian Perindustrian, 2017.
K. Perindustrian, "Rencana Induk Pembangunan Industri Nasional 2015-2035," ed. Jakarta, Indonesia: Pusat Dokumentasi Publik, 2015.
H. Kagermann, W.-D. Lukas, and W. Wahlster, "Industrie 4.0: Mit dem Internet der Dinge auf dem Weg zur 4. industriellen Revolution," VDI nachrichten, vol. 13, 2011.
M. Hermann, T. Pentek, and B. Otto, "Design Principles for Industrie 4.0 Scenarios: A Literature Review. Technische Universitat Dortmund," working paper2015.
H. Kagermann, J. Helbig, A. Hellinger, and W. Wahlster, Recommendations for implementing the strategic initiative INDUSTRIE 4.0: Securing the future of German manufacturing industry; final report of the Industrie 4.0 Working Group: Forschungsunion, 2013.
M. Cotteleer and B. Sniderman, "The forces of change: Industry 4.0," Deloitte Insights, December, vol. 18, p. 2017, 2017.
R. Geissbauer, J. Vedso, and S. Schrauf, "Industry 4.0: Building the digital enterprise," Retrieved from PwC Website: https://www. pwc. com/gx/en/industries/industries-4.0/landing-page/industry-4.0-building-your-digital-enterprise-april-2016. pdf, 2016.
C. J. Bartodziej, "The concept industry 4.0," in The Concept Industry 4.0, ed: Springer, 2017, pp. 27-50.
S. J. Russell and P. Norvig, Artificial intelligence: a modern approach, 3rd ed. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 2009.
D. H. Autor, "Why are there still so many jobs? The history and future of workplace automation," Journal of Economic Perspectives, vol. 29, pp. 3-30, 2015.
K. Schwab, "The fourth industrial revolution," in World Economic Forum. New York: Crown Business, 2016.
H. Boyes, B. Hallaq, J. Cunningham, and T. Watson, "The industrial internet of things (IIoT): An analysis framework," Computers in Industry, vol. 101, pp. 1-12, 2018.
J. Guiochet, M. Machin, and H. Waeselynck, "Safety-critical advanced robots: A survey," Robotics and Autonomous Systems, vol. 94, pp. 43-52, 2017.
F. Ingrand and M. Ghallab, "Deliberation for autonomous robots: A survey," Artificial Intelligence, vol. 247, pp. 10-44, 2017.
V. Beal. (2016, 19 Agustus). Wearable technology. Available: https://www.webopedia.com/TERM/W/wearable_technology.html
W.-Y. Yeong, C.-K. Chua, K.-F. Leong, M. Chandrasekaran, and M.-W. Lee, "Indirect fabrication of collagen scaffold based on inkjet printing technique," Rapid Prototyping Journal, vol. 12, pp. 229-237, 2006.
Q. Yan, H. Dong, J. Su, J. Han, B. Song, Q. Wei, et al., "A Review of 3D Printing Technology for Medical Applications," Engineering, 2018.
Lee, "Building Toward a Modern Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Sector : Encouraging Development and Adoption of Emerging Technology," F. C. f. D. E. a. Research, Ed., ed. United States of America: FDA, 2015.
S. Xue, P. Lv, Y. Wang, Y. Zhao, and T. Zhang, "Three dimensional bioprinting technology of human dental pulp cells mixtures," Journal of Peking University. Health sciences, vol. 45, pp. 105-108, 2013.
J. W. Stansbury and M. J. Idacavage, "3D printing with polymers: Challenges among expanding options and opportunities," Dental Materials, vol. 32, pp. 54-64, 2016.
J. Markarian. (2018, 6 Agustus 2018). Modernizing Pharma Manufacturing. Available: http://www.pharmtech.com/modernizing-pharma-manufacturing
S. C. Gad, Pharmaceutical manufacturing handbook: production and processes vol. 5: John Wiley & Sons, 2008.
S. Ibrić, Z. ćurić, J. Parojćić, and J. Petrović, "Artificial intelligence in pharmaceutical product formulation: neural computing," Chemical Industry and Chemical Engineering Quarterly, vol. 15, pp. 227-236, 2009.
C. da Costa, C. Mendes, and R. Osaki, "Industry 4.0 In Automated Production," 2017.
B. Ding, "Pharma industry 4.0: Literature review and research opportunities in sustainable pharmaceutical supply chains," Process Safety and Environmental Protection, vol. 119, pp. 115-130, 2018.
S. A. Narayana, R. K. Pati, and P. Vrat, "Managerial research on the pharmaceutical supply chain–A critical review and some insights for future directions," Journal of Purchasing and Supply Management, vol. 20, pp. 18-40, 2014.
R. Limaye, L. Kumar, and N. Limaye, "Fourth generation technologies in pharmaceuticals-Revolutionizing healthcare," Journal of Systems Biology & Proteome Research, vol. 2, 2018.
S. J. Trenfield, A. Awad, A. Goyanes, S. Gaisford, and A. W. Basit, "3D printing pharmaceuticals: drug development to frontline care," Trends in pharmacological sciences, 2018.
A. Goyanes, A. B. Buanz, G. B. Hatton, S. Gaisford, and A. W. Basit, "3D printing of modified-release aminosalicylate (4-ASA and 5-ASA) tablets," European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, vol. 89, pp. 157-162, 2015.
JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik (Journal of Industrial and Logistics Management) is an Open Access Journal. The authors who publish the manuscript in JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik agree to the following terms:

JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. This permits anyone to copy, redistribute, remix, transmit and adapt the work provided the original work and source is appropriately cited.
This means:
(1) Under the CC-BY license, authors retain ownership of the copyright for their article, but authors grant others permission to use the content of publications in JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik in whole or in part provided that the original work is properly cited. Users (redistributors) of JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik are required to cite the original source, including the author's names, JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik as the initial source of publication, year of publication, volume number, issue, and Digital Object Identifier (DOI); (2) Authors grant JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik the right of first publication. Although authors remain the copyright owner.