ANALISIS KEBIJAKAN INVENTORI PADA KOMPONEN DARAH PACKED RED CELL (PRC)
Downloads
Abstract
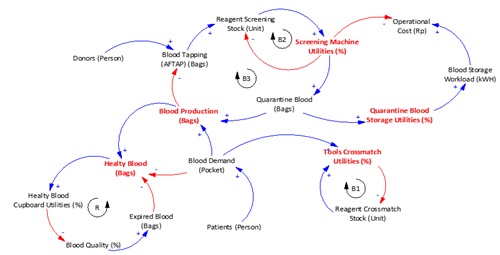
By following WHO guidelines, the minimum blood availability is 2% of the population. The total population of Indonesia in 2016 is 261.115.456, so ideally it takes 5.222.309 blood bags. In 2013-2015 for 36 months, there were 26 overstock events and 10 stockout events. The data shows that the frequency of over-supply is more frequent than over-demand. The high overstock has an impact on the high costs incurred by the City of Bandung PMI, if there is overstock there are two costs to be incurred, namely the cost of storing if the blood is still in good use and the cost of overstock if the blood is more than the expiration date. The purpose of this study was to determine the optimal value of inventory levels to reduce wastage of blood culling due to overstock occurring at PMI Bandung. The research method uses a quantitative approach to the optimization model of inventory policy, namely Uncertainty EOQ. The optimal amount of supplies that must be provided is at intervals of 8,705 - 9,375 blood bags with a large safety stock 403 blood bags and the ordering point is at the level of supplies of 5.706 blood bags. This proposal can provide a total inventory cost savings of Rp6.622.659.034/year.
Keywords: Blood, Overstock, EOQ, Uncertainty
Abstrak
Sesuai dengan panduan WHO, ketersediaan darah minimal adalah 2% dari jumlah penduduk. Jumlah penduduk Indonesia tahun 2016 adalah 261.115.456 jiwa, maka idealnya dibutuhkan 5.222.309 kantong darah. Tahun 2013-2015 selama 36 bulan, terdapat 26 kejadian overstock dan 10 kejadian stoc-kout. Data tersebut menunjukan bahwa frekuensi over-supply lebih sering dibandingkan over-demand. Tingginya overstock berdampak pada tingginya biaya yang dikeluarkan oleh PMI Kota Bandung, jika terjadi overstock ada dua biaya yang harus dikeluarkan, yaitu biaya simpan jika darah masih dalam masa baik digunakan dan biaya overstock jika darah sudah lebih dari tanggal kadaluarsa. Tujuan penelitian ini adalah mengetahui nilai tingkat persediaan yang optimal untuk mengurangi pemborosan pemusnahan darah akibat overstock yang terjadi di PMI Kota Bandung. Metode penelitian menggunakan pendekatan kuantitatif model optimasi pada kebijakan inventori yaitu EOQ Tak Tentu Berisiko Terkendali. Jumlah persediaan optimal yang harus disediakan berada di interval 8.705 – 9.375 kantong darah dengan besar safety stock 403 kantong darah dan titik pemesanan berada di tingkat persediaan 5.706 kantong darah. Usulan ini dapat memberikan penghematan total biaya persediaan sebesar Rp6.622.659.034/tahun.
Kata kunci: Darah, Overstock, EOQ, Tak Tentu
Downloads
E. C. Pearce, Anatomi dan Fisiologi untuk Paramedis, Jakarta: PT. Gramedia Pustaka Utama, 2009.
C. Brooker, Ensiklopedia Keperawatan, Jakarta EGC, 2009.
S. N. Bahagia, Sistem Inventori, Bandung: Penerbit ITB, 2006.
R. I. Kemkes, "InfoDATIN Pusat Data dan Informasi," in Situasi Pelayanan Darah di Indonesia, Jakarta, PMI, 2015.
T. Simatupang, "beritagar.id," Selasa September 2018. [Online]. Available: https://beritagar.id/artikel/berita/indonesia-masih-kekurangan-stok-darah. [Accessed Minggu November 2019].
BPS JABAR, "Badan Pusat Statitik Provinsi Jawa Barat," Senin Maret 2018. [Online]. Available: https://jabar.bps.go.id/statictable/2018/03/12/294/rekapitulasi-penerimaan-dan-pemakaian-darah-di-udd-pmi-menurut-kabupaten-kota-di-jawa-barat-2013-2016.html. [Accessed MInggu November 2019].
S. D. I. Gotama, G. Abdillah and A. I. Hadiana, "Perancangan Data Warehouse Unit Donor Darah Pada Palang Merah Indonesia Kota Bandung," Prosiding SNST FT Universitas Wahid Hasyim Semarang, vol. 7, 2016.
S. Nahdiyan, "Peran Sistem Informasi Akuntansi Persediaan Peralatan Medis Dalam Menunjang Efektivitas Kerja Karyawan Unit Donor Darah PMI," Widyatama Repository, Bandung, 2012.
Palang Merah Indonesia Kota Bandung, "Laporan Kegiatan Tahun 2013 PMI Kota Bandung," PMI Kota Bandung, Bandung, 2015.
Palang Merah Indonesia Kota Bandung, "Laporan Kegiatan Tahun 2014 PMI Kota Bandung," PMI Kota Bandung, Bandung, 2015.
Palang Merah Indonesia Kota Bandung, "Laporan Kegiatan Tahun 2015 PMI Kota Bandung," PMI Kota Bandung, Bandung, 2017.
S. Kodu, "Harga, Kualitas Produk dan Kualitas Pelayanan Pengaruhnya Terhadap Keputusan Pengambilan Mobil Toyota Avanza," EMBA, vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 1251-1259, 2013.
F. Ramadhona and N. B. Puspitasari, "Analisis Usulan Penentuan Optimal Ordering Cost Cover Engine YA40003084 Untuk Minimasi Total Inventory Cost Dengan Metode Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)," Industrial Engineering Online Journal, vol. 5, no. 4, 2016.
W. Akhdemila, "Analisis Pengendalian Persediaan Darah Pada Palang Merah Indonesia (PMI) Unit Transfusi Darah Cabang (UTDC) Kota Depok," Program Sarjana IPB, Bogor, 2009.
A. Wulandari, D. D. Damayanti and B. Santosa, "Penentuan Kebijakan Persediaan Suku Cadang Pada Produk Amonia dan Urea di PT. XYZ untuk Meminimasi Total Biaya Persediaan dengan Pendekatan Metode Inventori Tak Tentu Berisiko Terkendali," Jurnal Rekayasa Sistem & Industri, vol. 1, no. 1, 2014.
R. E. Walpole, R. H. Myers, S. L. Myers and K. Ye, Probability & Statistics for Engineers & Scientists Ninth Edition, USA: Pearson Eduation Inc, 2012.
Y. M. K. Aritonang, M. Nainggolan and K. P. Ariningsih, "Perancangan Strategi Manajemen Persediaan Darah di PMI Bandung," LPPM UNPAR, Bandung, 2016.
A. Sumbar, "Antaranews.com," Senin Maret 2015. [Online]. Available: https://sumbar.antaranews.com/berita/142706/rs-keluhkan-tingginya-biaya-pengelolaan-limbah-medis. [Accessed Selasa Februari 2018].
D. Tanamal, "Jawaban.Com," Senin Maret 2015. [Online]. Available: https://www.jawaban.com/read/article/id/2015/03/16/236/150317102049/7-Dampak-Buruk-Akibat-Salah-Mengelola-Keluhan-Pelanggan. [Accessed Kamis Maret 2018].
JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik (Journal of Industrial and Logistics Management) is an Open Access Journal. The authors who publish the manuscript in JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik agree to the following terms:

JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. This permits anyone to copy, redistribute, remix, transmit and adapt the work provided the original work and source is appropriately cited.
This means:
(1) Under the CC-BY license, authors retain ownership of the copyright for their article, but authors grant others permission to use the content of publications in JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik in whole or in part provided that the original work is properly cited. Users (redistributors) of JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik are required to cite the original source, including the author's names, JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik as the initial source of publication, year of publication, volume number, issue, and Digital Object Identifier (DOI); (2) Authors grant JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik the right of first publication. Although authors remain the copyright owner.