PERANCANGAN SISTEM INFORMASI BASIS DATA INVENTARIS BARANG BERBASIS WEB MENGGUNAKAN MODEL WATERFALL
Downloads
Abstract
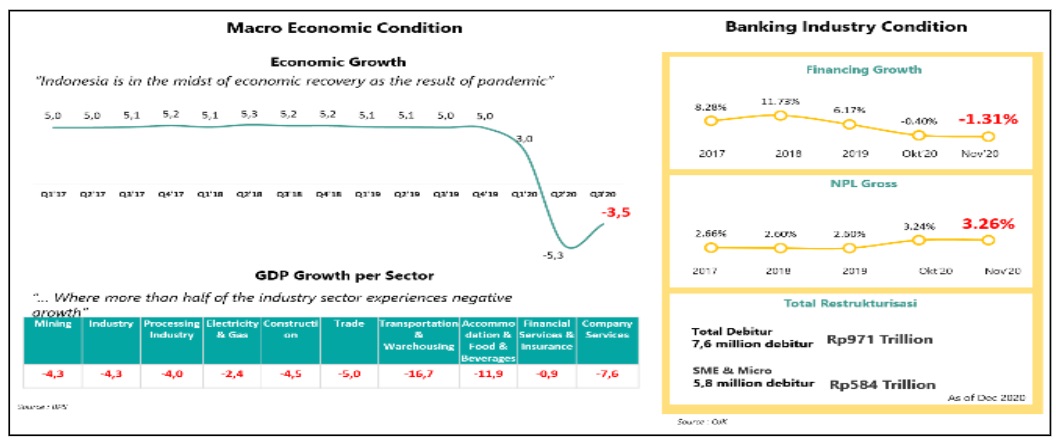
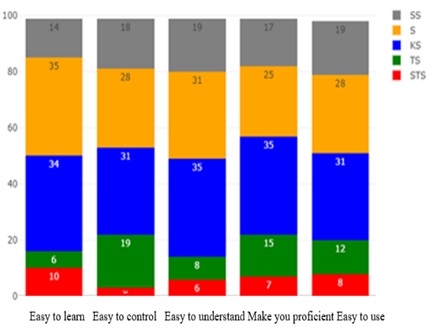
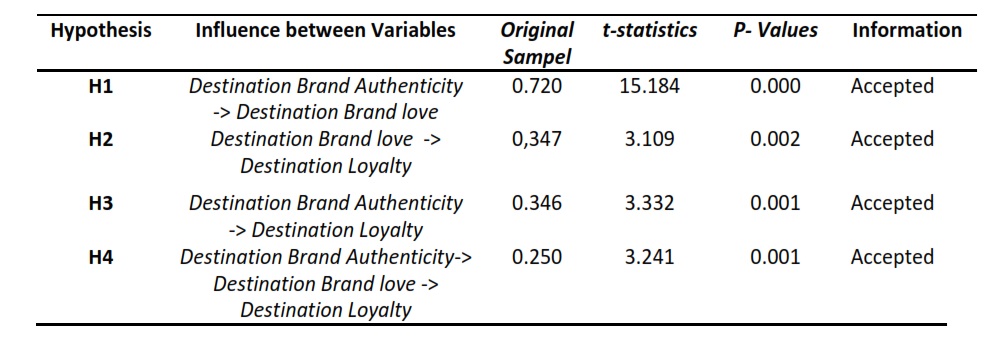
Good inventory management requires support from a database information system. The problem that occurs in the Untirta Industrial Engineering laboratory is that the inventory management system is still traditional method, that is data recording is done individually so that the existing data overlaps and results in invalid information. The purpose of this research is to design a database information system. The Waterfall model is used for design. This method consists of the analysis phase, the design phase, the implementation phase, the test phase and the maintenance phase. The results obtained from the analysis phase are the functional requirements for logging in users and data engineering requirements such as add, view, delete. The design phase uses DFD and ERD. Based on the context diagram, the external agents involved are the admin (head of the laboratory) and user (laboratory assistant). The design results that have been implemented through a web-based interface are then tested using a blackbox test and usability test. The test results state a value of 86% which means the results are in very good classification.
Abstrak
Pengelolaan barang inventaris yang baik membutuhkan dukungan dari sistem informasi basis data. Masalah yang terjadi di laboratorium jurusan Teknik Industri Untirta adalah sistem pengelolaan barang inventaris masih bersifat tradisional, yaitu pencatatan yang dilakukan sendiri-sendiri sehingga data yang ada tumpang tindih dan menghasilkan informasi yang kurang valid. Tujuan dari penelitian ini adalah merancang sistem informasi basis data. Model Waterfall digunakan untuk perancangan. Metode ini terdiri dari tahap analisis, tahap desain, tahap implementasi, tahap uji dan tahap pemeliharaan. Hasil yang didapatkan dari tahap analisis adalah adanya kebutuhan fungsional untuk log in user dan kebutuhan rekayasa data seperti tambah, lihat, hapus. Tahap desain menggunakan DFD dan ERD. Berdasarkan diagram konteks, agen eksternal yang terlibat adalah admin (kepala laboratorium) dan user (asisten laboratorium). Hasil desain yang telah diimplementasikan melalui tampilan antar-muka berbasis web kemudian diuji menggunakan uji blackbox dan uji usability. Hasil uji menyatakan nilai sebesar 86% yang berarti hasil berada dalam klasifikasi sangat baik.
Downloads
K. L. Berg, T. Seymour, and R. Goel, "History Of Databases,” Int. J. Manag. Inf. Syst., vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 29–36, 2012, doi: 10.19030/ijmis.v17i1.7587.
M. A. Rather and V. Bhatnagar, "A comprative study of sdlc model,” no. October 2015, 2016.
M. STOICA, M. MIRCEA, and B. GHILIC-MICU, "Software Development: Agile vs. Traditional,” Inform. Econ., vol. 17, no. 4/2013, pp. 64–76, 2013, doi: 10.12948/issn14531305/17.4.2013.06.
D. W. W. Royce, "Managing the Development of large Software Systems,” Ieee Wescon, no. August, pp. 1–9, 1970.
S. T. ind, Karambir, "A Simulation Model for the Spiral Software Development Life Cycle,” Int. J. Innov. Res. Comput. Commun. Eng., vol. 03, no. 05, pp. 3823–3830, 2015, doi: 10.15680/ijircce.2015.0305013.
Y. Firmansyah and U. Udi, "Penerapan Metode SDLC Waterfall Dalam Pembuatan Sistem Informasi Akademik Berbasis Web Studi Kasus Pondok Pesantren Al-Habib Sholeh Kabupaten Kubu Raya, Kalimantan Barat,” J. Teknol. dan Manaj. Inform., vol. 4, no. 1, 2017, doi: 10.26905/jtmi.v4i1.1605.
A. Stellman and J. Greene, "Applied Software Project Management: Estimation,” pp. 1–14, 2014.
R. Inggi, B. Sugiantoro, and Y. Prayudi, "Penerapan System Development Life Cycle ( Sdlc ) Dalam ( Sdlc ) Dalam Mengembangkan,” no. December, 2018, doi: 10.5281/zenodo.2528444.
R. Tullah and M. I. Hanafri, "Evaluasi Penerapan Sistem Informasi Pada Politeknik LP3I Jakarta Dengan Metode Pieces,” J. Sisfotek Glob., vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 22–28, 2014.
J. Anfa and D. Chalidyanto, "Evaluasi Kinerja Billingsystem Rawat Inap Menggunakan Kerangka Pieces,” J. Adm. Kesehat. Indones., vol. 4, no. 1, p. 18, 2016, doi: 10.20473/jaki.v4i1.2016.18-27.
J. Satzinger, Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing Word Fifth Edition. 2010.
M. A. B. M. Hussain, A. S. Baharudin, and K. Karkonasasi, "USM internship and career portal,” Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res., vol. 11, no. 20, pp. 10247–10251, 2016.
D. Yeates and T. Wakefield, Systems Analysis and Design 2nd Edition. 2004.
T. S. Jaya, "Pengujian Aplikasi dengan Metode Blackbox Testing Boundary Value Analysis (Studi Kasus: Kantor Digital Politeknik Negeri Lampung),” J. Inform. Pengemb. IT, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 45–46, 2018, doi: 10.30591/jpit.v3i1.647.
A. Bangor, T. Staff, P. Kortum, J. Miller, and T. Staff, "Determining what individual SUS scores mean: adding an adjective rating scale,” Determ. what Individ. SUS scores mean adding an adjective Rat. scale, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 114–123, 2009.
JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik (Journal of Industrial and Logistics Management) is an Open Access Journal. The authors who publish the manuscript in JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik agree to the following terms:

JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. This permits anyone to copy, redistribute, remix, transmit and adapt the work provided the original work and source is appropriately cited.
This means:
(1) Under the CC-BY license, authors retain ownership of the copyright for their article, but authors grant others permission to use the content of publications in JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik in whole or in part provided that the original work is properly cited. Users (redistributors) of JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik are required to cite the original source, including the author's names, JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik as the initial source of publication, year of publication, volume number, issue, and Digital Object Identifier (DOI); (2) Authors grant JMIL Jurnal Manajemen Industri dan Logistik the right of first publication. Although authors remain the copyright owner.